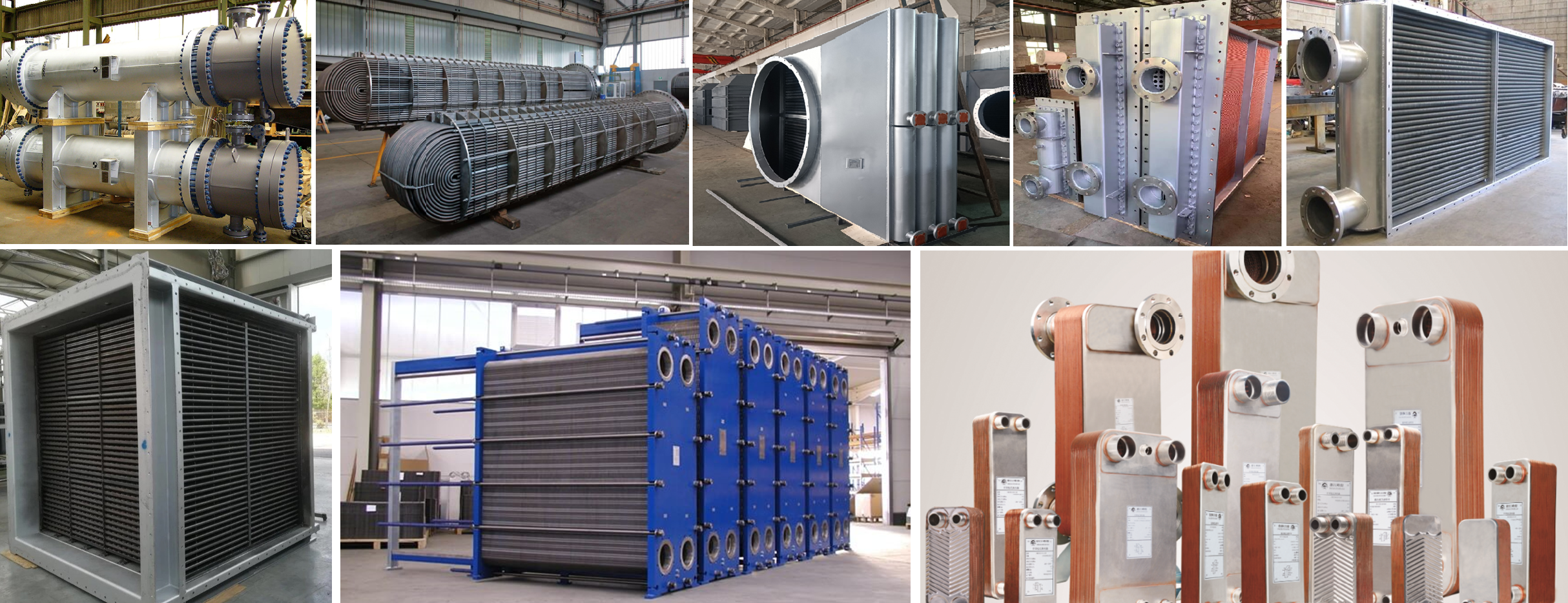
Fins tube heat exchanger
Thompson Heat Transfer Fin-tube heat exchangers typically use air to cool or heat a fluid such as air, water, oil or gas, or they can be used to capture or recover waste heat. These heat exchangers can be used in a variety of industries including oil and gas, power generation, marine and HVAC&R.
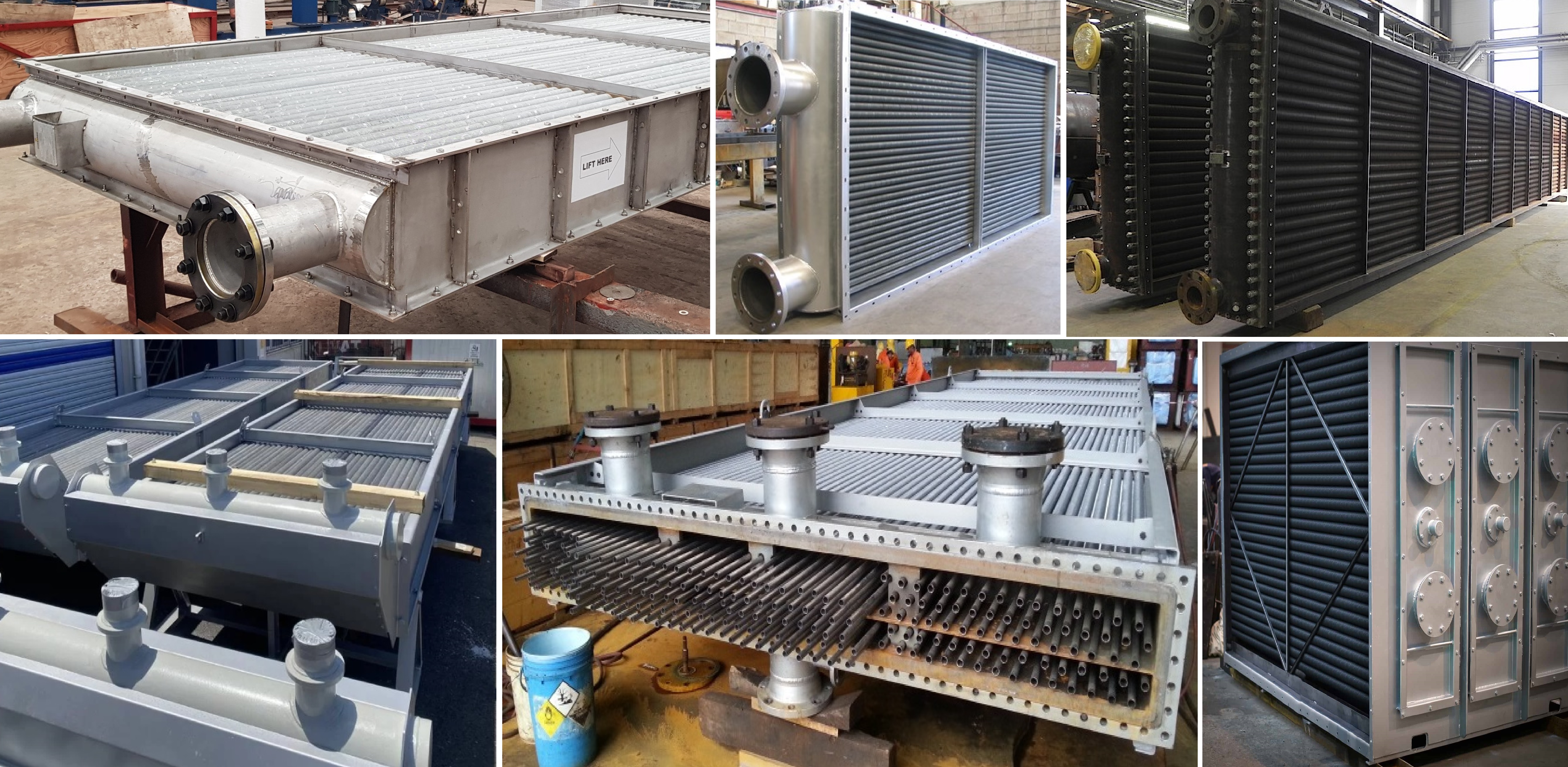

Fin-tube heat exchangers have many applications, some of which are:
- Diesel charge air coolers;
- Oil coolers;
- Hydrogen coolers;
- waste heat recovery;
- dryers;
- air conditioners;
- air heaters;
- steam condensers;
- generator coolers
Fin-tube heat exchangers are typically used where air is the preferred medium for cooling or heating, especially when water is scarce or of poor quality.
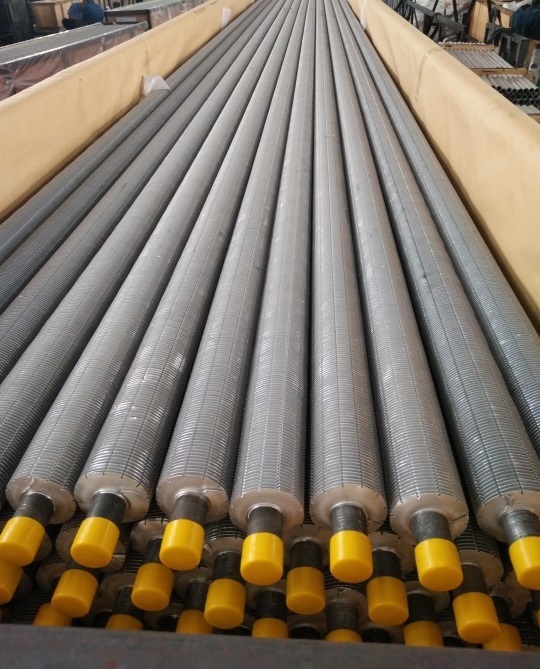
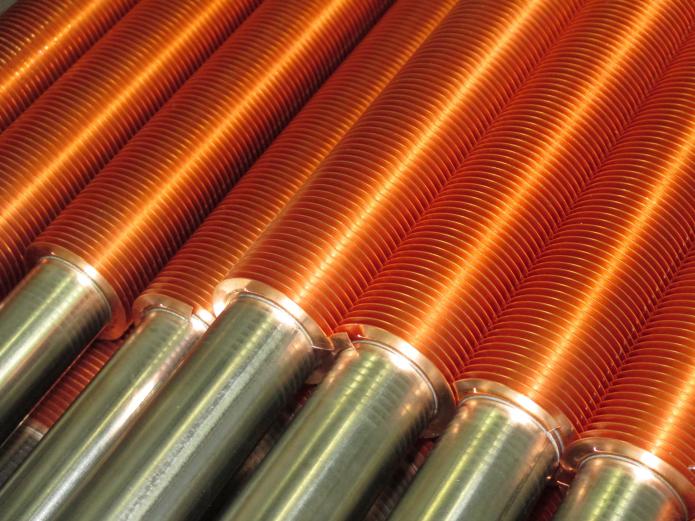
In a finned tube heat exchanger, heat is exchanged between a thermally efficient, heat-transporting fluid, such as a viscous fluid, and a non-viscous fluid, such as air or a low-density gas. On the ‘air side’, the tube surface is enhanced by the addition of fins or other components such as wire loops, designed to increase the surface area of the tube and improve the thermal performance of the tube.
The fins can be of varying heights (high fin to low fin) and the fins can be pressure-bonded to the outer surface of the tube or formed into the tube surface.
Depending on the intended task and the environment in which they operate, finned tubes can be manufactured in a variety of designs and incorporate a variety of materials for both the tube and the fins. The types and combinations of tubes and fins are important, but in this article we will only explore the most common types.
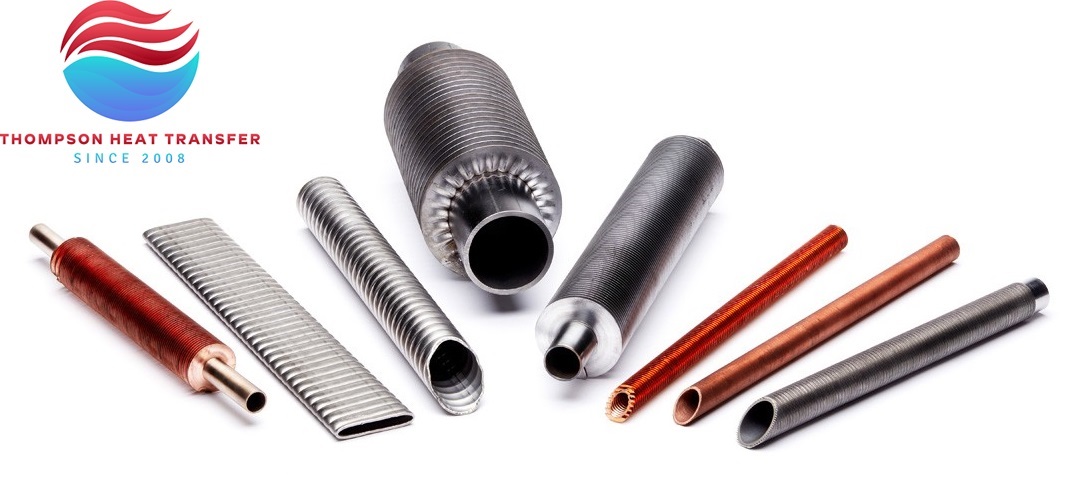

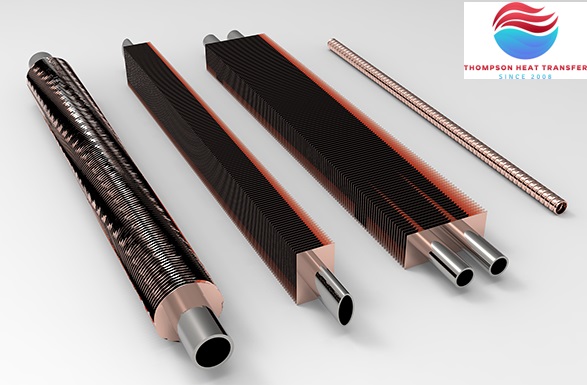
Fin Profile
The profile of the fins has significant effect of the performance of a finned tube heat exchanger. It is important to ensure each fin has a tight connection on the tube surface to provide maximum thermal conductivity.
The larger the fins and the tighter the fin pitch, the more thermal conductivity is achieved. The trade-off may be an increase in pressure drop which may, in turn, adversely affect performance. A balance between the two opposing functions is vital for effective and optimal thermal performance and equipment function.


There are many variables to be considered to successfully select and design a finned tube heat exchanger including:
- the duty to be performed;
- type, style and number of tubes required;
- metals best suited for the tubes and the fins;
- type of tube enhancement – fins or wire;
- thickness of the tube walls;
- I/D and O/D of the tubes;
- pitch of the fins;
- type and number of fans to provide air flow;
- the environment in which the heat exchanger is to be used and
- the duty it is required to perform
To ensure you get the best finned tube heat exchanger for your needs requires high-end software calculations, experience and technical know-how to bring it all together into a reliable unit that will provide years of efficient and reliable service.
Please contact us to inspect and get suitable design.

